Did You Know?
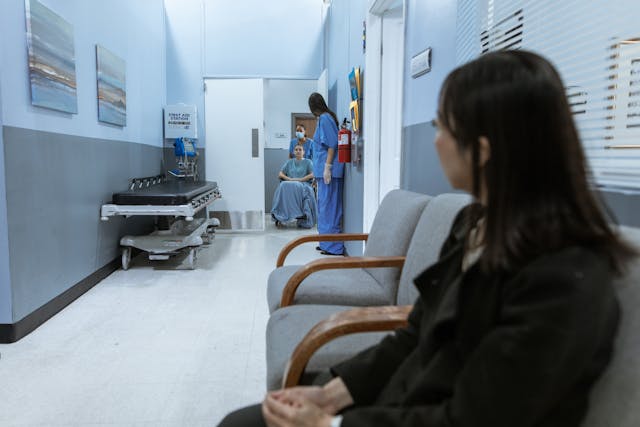

Unsanitary practices in nursing homes significantly compromise the health and well-being of elderly residents. Infections are a prevalent concern, with over 1.5 million people residing in approximately 16,000 U.S. nursing facilities, making infection control paramount. Alarmingly, more than 1,300 nursing homes experienced infection rates of 75% or higher
Pressure ulcers, often resulting from inadequate hygiene and care, affect about 11% of nursing home residents, leading to increased medical complications and mortality. Moreover, studies indicate that nursing homes frequently underreport the incidence and severity of pressure ulcers, raising concerns about the reliability of self-reported data on patient safety. These statistics underscore the urgent need for stringent infection control measures and accurate reporting to safeguard the health of seniors in care facilities.
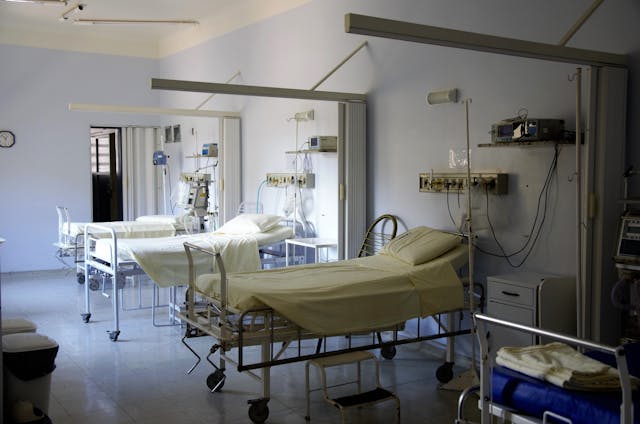
Unsanitary bedding and dirty sheets in senior care facilities can have severe health consequences, particularly for elderly residents with limited mobility. Prolonged exposure to soiled or unclean linens increases the risk of pressure ulcers (bedsores), skin infections, and respiratory issues due to bacteria, mold, and allergens.
According to the CDC, approximately 2.5 million people in the U.S. develop bedsores each year, with nursing home residents being among the most vulnerable. Poor hygiene practices can also lead to urinary tract infections (UTIs), pneumonia, and worsening chronic conditions, significantly impacting a senior’s overall well-being and quality of life. Ensuring clean and fresh bedding is a basic yet crucial aspect of elder care, helping to prevent infections, promote comfort, and maintain dignity for aging individuals.

Elder abuse within nursing homes and senior care facilities is a pervasive and underreported issue in the United States. Approximately 16% of residents in these settings report experiencing abuse, which can manifest physical, emotional, financial, or sexual mistreatment.
Alarmingly, a study by the World Health Organization found that 66% of nursing home staff admitted to committing some form of elder abuse in the past year.
In 2023, U.S. nursing homes received 94,499 health citations, with 8.1% (7,654) related to abuse, neglect, or exploitation of residents. These statistics underscore the urgent need for comprehensive reforms, increased oversight, and robust reporting mechanisms to protect vulnerable seniors in care facilities.
